Natural Language Processing and TensorFlow Implementation Across Industries
At the recent meetup in Madrid, the speakers recalled the outstanding use cases of TensorFlow adoption and overviewed how the library and the related tools can be applied to natural language processing.
(Featured image courtesy of Silicon Valley Data Science.)
What’s been done in 67 weeks
Gorka Bengochea of Ibermática walked the attendees through the memorable scenarios, where TensorFlow helped out, since it was open-sourced back in November 2015:
- Keeping track of sea cow population, which is under a threat of extinction, by automating the recognition process based on dozens of thousands aerial photos
- Automating the process of sorting cucumbers
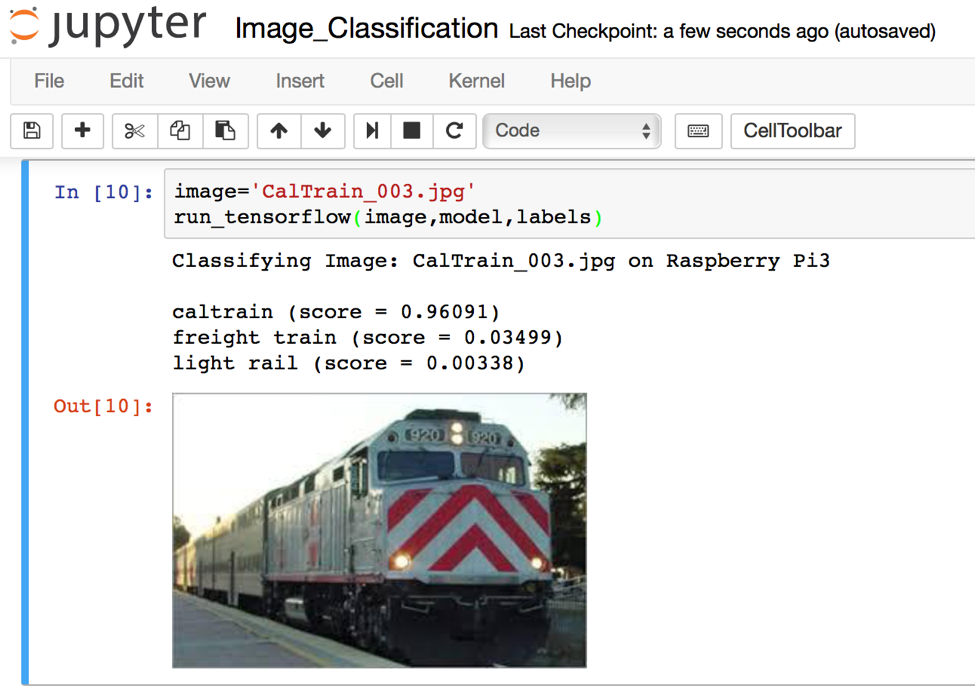
- Improving train arrival predictions
- Delivering an algorithm that can learn how to play 49 different arcade games, including the iconic Space Invaders, for instance (a project launched by DeepMind Lab, Google’s AI-centric subsidiary)
- Predict Alzheimer’s disease by integrating the Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) standard with TensorFlow (Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai)
For more detail, look through Gorka’s presentation below.
TensorFlow for Natural Language Processing
Santiago Saavedra of OpenShine investigated into how TensorFlow and the related tools from its ecosystem can be applied to carry out such natural language processing tasks as:
- part-of-speech (POS) tagging
- sentiment analysis
- machine translation, etc.
He also exemplified a number of tools and means to address the issues of producing word embeddings, language modeling, and machine translation.
Thus, long short-term memory networks can help to assign probabilities to sentences, predicting the next word in a text based on the given examples.
The seq2seq library is frequently used to enhance machine translation, while the word2vec algorithm is capable of transforming words in a corpus to vectors in a >100-dim space to make word embeddings. One can also make use of SyntaxNet, a natural language processing framework for TensorFlow.
You can find Santiago’s full presentation here. Join our group to stay tuned with the upcoming events.
Want details? Watch the video!
Further reading
- How TensorFlow Can Help to Perform Natural Language Processing Tasks
- The Magic Behind Google Translate: Sequence-to-Sequence Models and TensorFlow
- Analyzing Text and Generating Content with Neural Networks and TensorFlow
About the experts
Gorka Bengochea is passionate about innovation and artificial intelligence. An engineering student at Madrid Polytechnical University, he has worked at the Ed-tech startup in Silicon Valley and initiated the deep learning line of Ibermática, a Spain-based consulting company.
Santiago Saavedra is a hacker at OpenShine and an enthusiast with a passion for computer science and open source. He’s been engaged in many subfields of Computer Science, from collaborative edition in distributed systems to formal methods for software verification.