IoT Platform on Bluemix: Experimenting with IBM Watson and Gobot

The demo app described in this post consists of two main components:
- A “sensor” that collects various information about a MacBook laptop: CPU temperature, fan speed, and laptop position using the Sudden Motion Sensor
- A web application that visualizes data from the sensor and allows you to set fan speed and display brightness
Prerequisites
To follow the instructions, you need:
- A Bluemix account
- The Cloud Foundry CLI
The source code for the demo is available here.
Preparing Internet of Things Platform
- Clone my repository.
- Create a Go web application from the Bluemix dashboard.
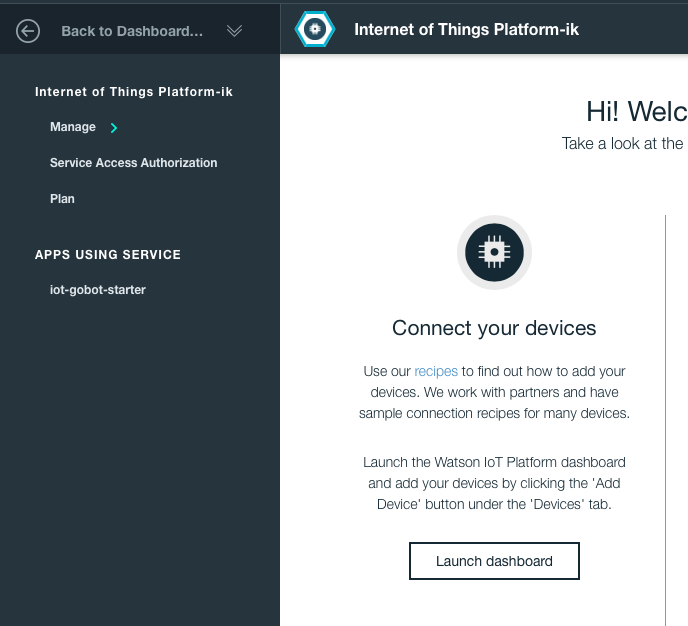
- Create an instance of the Internet of Things Platform service:
- Click Internet of Things Platform on the Bluemix dashboard.
- Click Launch dashboard.
- Create a new device on the IoT Platform dashboard.
- From the sensor directory, run the
go buildcommand and then thesudo ./sensor -id id you provided when creating the device -org organization id -api_token authentication tokencommand. The Organization ID and Authentication Token are shown after your create a device. - Go to the repository directory and run the
cf push application namecommand. See step 2. - Open the application in a browser and provide the device ID.

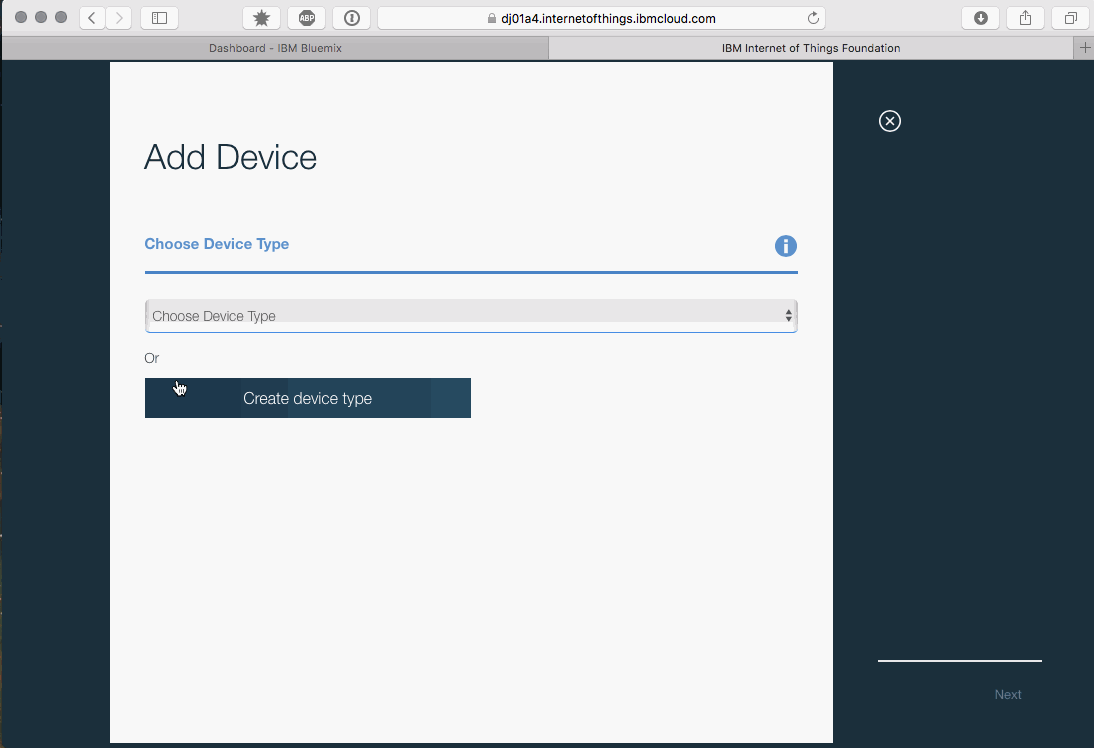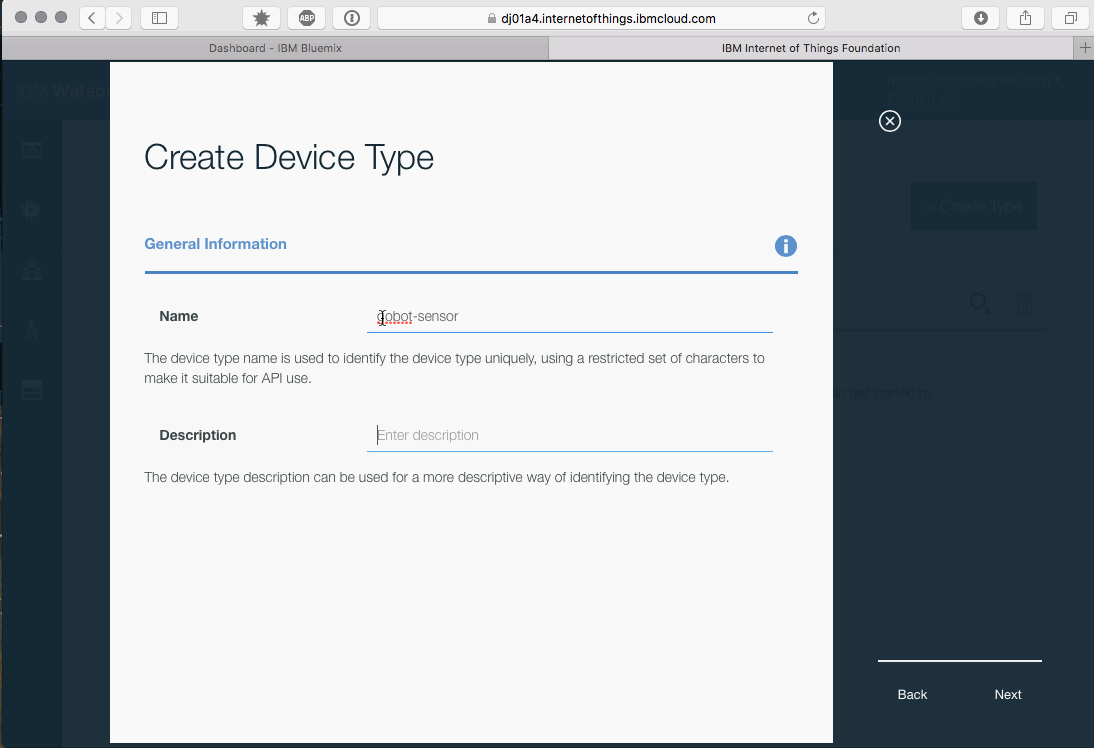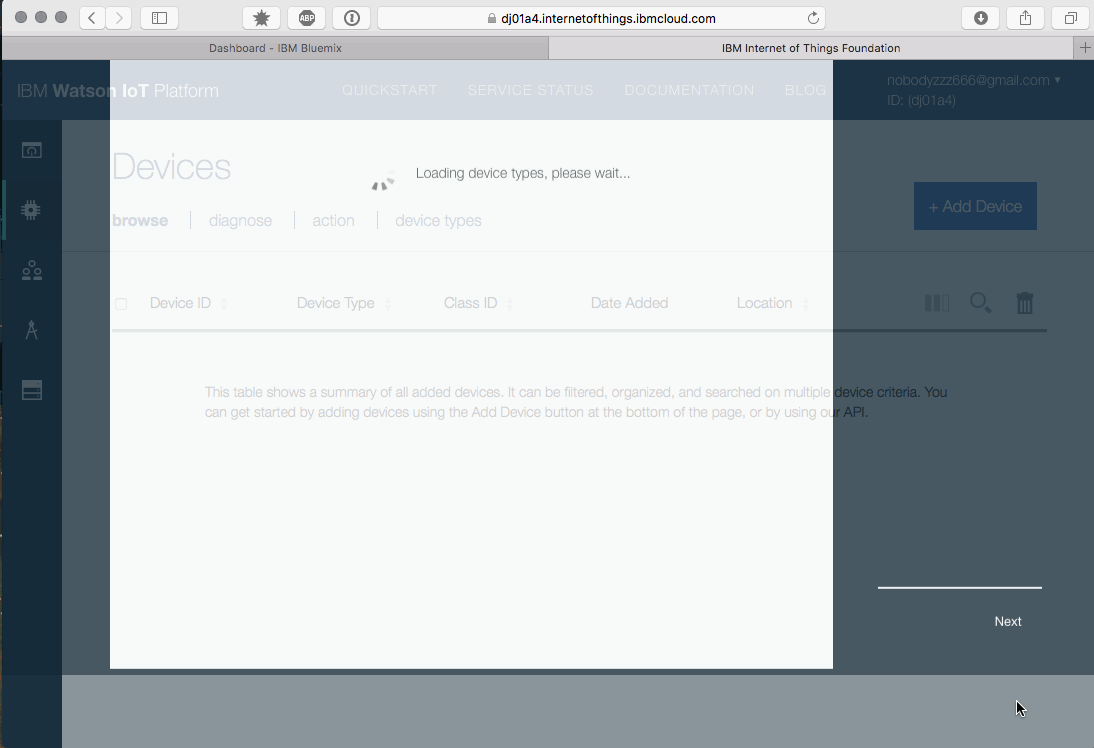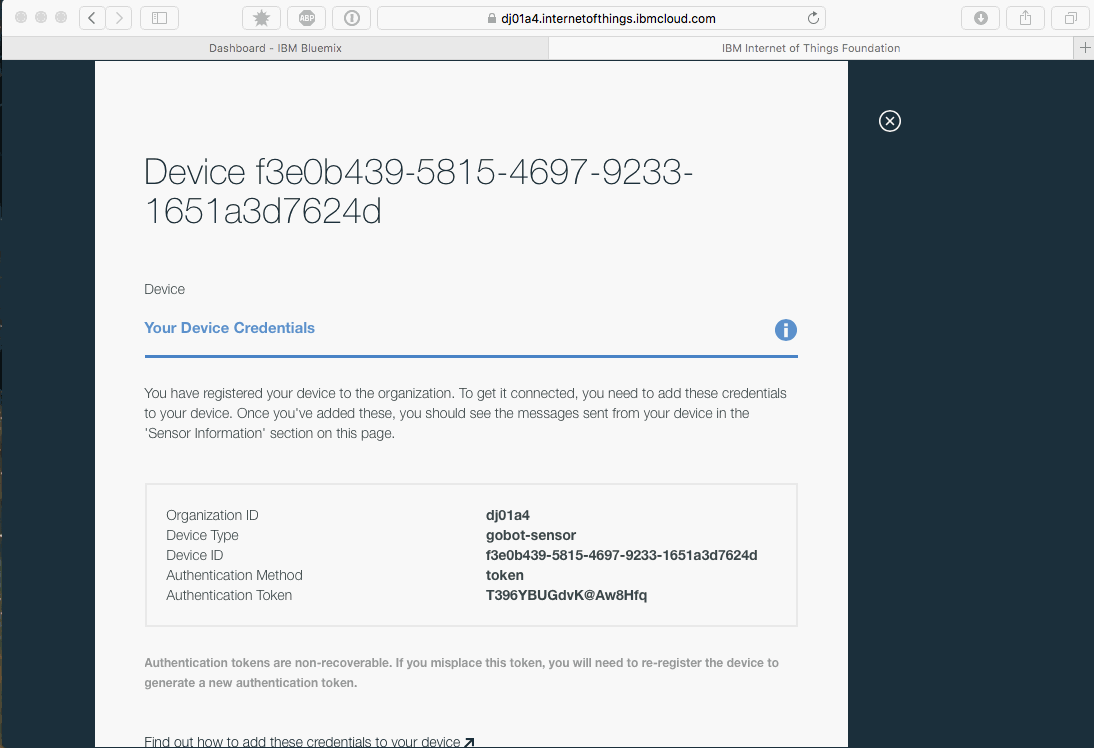
Connecting a device to the IoT platform
Every registered organization has a unique endpoint that must be used when connecting MQTT clients for devices in that organization:
1 | org_id.messaging.internetofthings.ibmcloud.com |
You can find your org_id on the IoT Platform dashboard.

A device must authenticate using a client ID in the following format:
1 | D:org_id:device_type:device_id |
where:
didentifies your client as a device.org_idis your unique organization ID.type_idis the device type you specified when creating the device on the dashboard.device_idis the ID you specified when creating the device on the dashboard.
The Watson IoT platform currently only supports token-based authentication for devices, so there is only one valid username for them—use-token-auth. Use the authentication token generated by the platform upon device creation as a password.
Connecting your Gobot sensor to the IoT platform should look similar to:
1 2 3 | mqttAdaptor := mqtt.NewMqttAdaptorWithAuth("sensor", fmt.Sprintf("tcp://%s.messaging.internetofthings.ibmcloud.com:1883", *org), fmt.Sprintf("d:%s:gobot-sensor:%s", *org, *deviceId), username, *apiToken) |
Publishing device events
Devices can only publish to the event topic:
1 | iot-2/evt/event_id/fmt/format_string |
where:
event_idis the ID of the event, for examplestatus. The event ID can be any string permitted by MQTT. Subscriber applications must use this string in their subscription topic to receive the events published on this topic if wildcards are not used.format_stringis the format of the event payload, for examplejson. The format can be any string permitted by MQTT. Subscriber applications must use this string in their subscription topic to receive events published on this topic if wildcards are not used.
For example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | gobot.Every(1*time.Second, func() { data, err := json.Marshal(GatherSensorInfo()) if err == nil { mqttAdaptor.Publish("iot-2/evt/status/fmt/json", data) } }) |
Subscribing to commands
To receive a command, your device has to subscribe to command topics:
1 | iot-2/cmd/command_id/fmt/format_string |
where:
command_idis the ID of the command, for exampleupdate. The command ID can be any string permitted by MQTT. A device must use this string in its subscription topic to receive commands published on this topic if wildcards are not used.format_stringis the format of the event payload, for examplejson. The format can be any string permitted by MQTT. A device must use this string in its subscription topic to receive commands published on this topic if wildcards are not used.
For example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | mqttAdaptor.On("iot-2/cmd/set_speed/fmt/json", func(data []byte) { var cmd SetSpeedCmd if err := json.Unmarshal(data, &cmd); err == nil { C.SMCSetFanSpeed(C.int(cmd.Fan), C.int(cmd.Speed)) } else { log.Printf("Error: %s", err) } }) mqttAdaptor.On("iot-2/cmd/inc_brightness/fmt/json", func(data []byte) { C.IncreaseBrightness() }) mqttAdaptor.On("iot-2/cmd/dec_brightness/fmt/json", func(data []byte) { C.DecreaseBrightness() }) |
Connecting an application to the IoT platform
An application has to use the same organization endpoint as your device. The application must authenticate using a client ID in the following format:
1 | a:org_id:app_id |
where:
aindicates the client is an application.org_idis your unique organization ID.app_idis a user-defined unique string identifier for this client.
You don’t need to register the application before it is connected, so app_id can be any string that follows these rules:
- Contains only alphanumeric characters (a-z, A-Z, 0-9) and hyphen (-), underscore (_), or dot (.)
- Has a maximum length of 36 characters
Applications need an API key to connect to an organization. When an API key is registered, a token will be generated and it must be used with that API key.
The API key looks similar to this: a-org_id-b2roh3bptq. The token looks similar to this: p3C76R-54EPKmeKCPA.
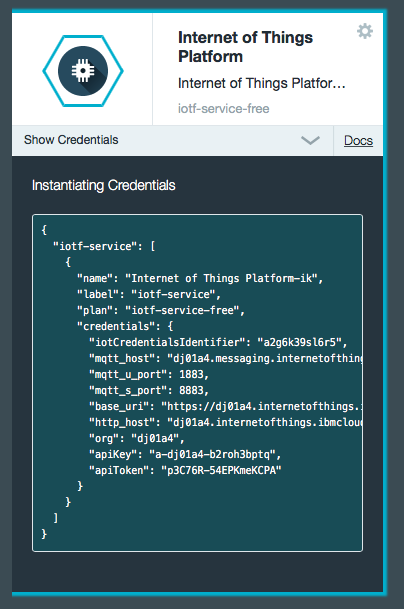
For example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | if appEnv, err := cfenv.Current(); err != nil { org = "quickstart" port = ":8080" } else { port = fmt.Sprintf(":%d", appEnv.Port) if iotfService, err := appEnv.Services.WithLabel("iotf-service"); err == nil { org = fmt.Sprintf("%s", iotfService[0].Credentials["org"]) apiKey = fmt.Sprintf("%s", iotfService[0].Credentials["apiKey"]) apiToken = fmt.Sprintf("%s", iotfService[0].Credentials["apiToken"].(string)) } } ... mqttAdaptor := mqtt.NewMqttAdaptorWithAuth("server", fmt.Sprintf("tcp://%s.messaging.internetofthings.ibmcloud.com:1883", org), fmt.Sprintf("a:%s:%s", org, uuid.Formatter(u, uuid.CleanHyphen)), apiKey, apiToken) |
Subscribing to device events
Subscribe to the topic:
1 | iot-2/type/device_type/id/device_id/evt/event_id/fmt/format_string |
The MQTT “any” wildcard character (+) may be used for any of the following components if you want to subscribe to more than one type of event or events from more than a single device:
device_typedevice_idevent_idformat_string
For example:
1 2 3 4 | mqttAdaptor.On(fmt.Sprintf("iot-2/type/+/id/%s/evt/+/fmt/json", deviceId), func(data []byte) { ... }) |
Publishing device commands
Your application can publish a command to any registered device. Publish to the topic:
1 | iot-2/type/device_type/id/device_id/cmd/command_id/fmt/format_string |
For example:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | cmdData, err := json.Marshal(cmd) if err == nil { mqttAdaptor.Publish(fmt.Sprintf("iot-2/type/gobot-sensor/id/%s/cmd/set_speed/fmt/json", deviceId), cmdData) } else { log.Printf("Error sending command: %s", err) } |
For more information about application and device communication, see IBM Watson IoT Platform Documentation.
As you can see, with MQTT support in Watson IoT Platform and Gobot, it is really easy to connect your devices and applications.