IBM: Blockchain to Transform IoT, Supply Chains, and the World Around Us
A secure enterprise-ready blockchain
IBM InterConnect 2017 has introduced many announcements from IBM and the company’s partners. Among the news was the reveal of IBM’s enterprise-grade blockchain service, which is based on the Linux Foundation’s Hyperledger Fabric v1.0. Available in the IBM Cloud, the blockchain is secured by IBM LinuxONE.
“We’re building a blockchain for trust for a very simple reason-so you can conduct your business securely, meet all those terms and conditions for your business network and regulatory requirements,” said Ross Mauri of IBM. “It’s also an infrastructure that’s Agile so you can meet your business transformation goals.”
“IBM Blockchain runs on the industry’s most secure Linux servers in the IBM cloud. It’s an architecture that’s built end-to-end for security and performance.” —Ross Mauri, IBM
“We’ve created an infrastructure where you write your application and worry about your business logic and blockchain network,” added Ross. “When it runs on our infrastructure, it inherits all the security transparently with zero code change and zero hit to performance.”
According to Ross, IBM Blockchain is safe even from government influence. “If the government came to IBM and subpoenaed us to give them your data, we couldn’t do that,” he said. “Only you have the keys to your data. Only you have access to it. Even IBM can’t get to it.”
What makes it different?
In previous posts, we’ve detailed what blockchains provide to supply chains. In short, these are the key characteristics that blockchain introduces:
- Consensus. All ledgers in the network are kept in sync and all agree to the whats and whens of a transaction.
- Provenance. There are records of where each asset has been.
- Immutability. Anything written on the ledger cannot be undone. This means you cannot delete records and you cannot insert them halfway through the blockchain.
- Finality. Anything written in the blockchain cannot be disputed.
So far, security in blockchain meant high availability and integrity. Encryption wasn’t in the picture yet.
“With IBM Blockchain, you can rapidly develop blockchain solutions. With a few clicks, you can find and govern your blockchain network. You can operate those networks with security and do it all at scale. You can analyze into those networks by peering in to gain additional insight.”
—Jerry Coumo, IBM
With the IBM Blockchain built on LinuxONE, that aspect of security changes. Being placed on a secure Linux server adds the following benefits:
- Protection from insider attacks. Helps to safeguard entry points on the network and fight insider threats from anyone with system administrator credentials.
- The Evaluation Assurance Level certification of EAL5+, which is critical in highly regulated industries, such as government, finance, and healthcare, to prevent the leakage of information between environments.
- Secure Service Containers. Help to protect code throughout the blockchain application, effectively encapsulating the blockchain into a virtual appliance, denying access even to privileged users.
- Tamper-responsive hardware security modules. Protects encrypted data for storage of cryptographic keys. These modules are certified to FIPS 140-2 Level 4, the highest level of security certification available for cryptographic modules.
- A highly auditable operating environment. Comprehensive log data supports forensics, audit, and compliance.
Along with IBM Blockchain was the introduction to Fabric Composer, a tool that “allows business users and developers to speak the same language, thereby accelerate the creation of busineses solutions from days to minutes,” according to Jerry Coumo. With it, blockchain creation and management has been simplified, as users can:
- Rapidly develop a blockchain solution
- Find and govern blockchain networks
- Operate those networks with security and do it all at scale
- Analyze into those networks by peering in to gain additional insight
Blockchain for shipping
During the event, various success stories of using IBM Blockchain were presented.
Earlier this month, IBM and Maersk announced a partnership aimed at improving global, cross-border supply chains with blockchain. The idea is to use blockchain to have optimal document workflow, real-time visibility, and reduced fraud.
“We believe that this new supply chain solution will be a transformative technology with the potential to completely disrupt and change the way global trade is done.” —Bridget van Kralingen, IBM
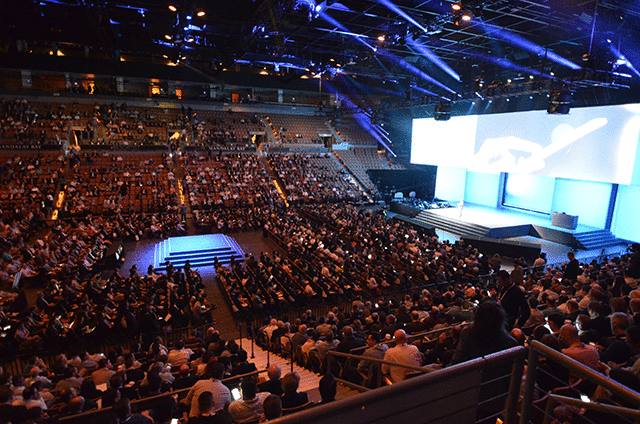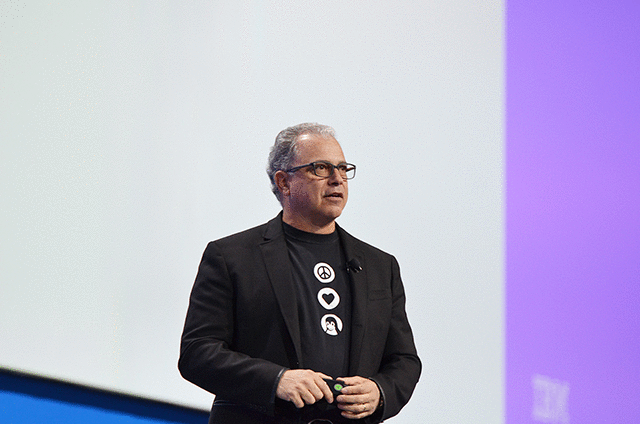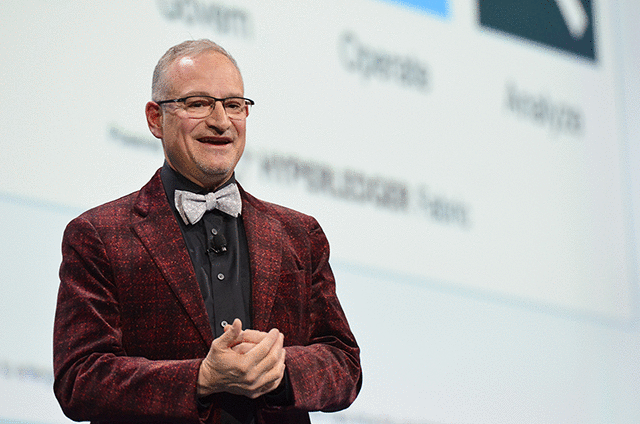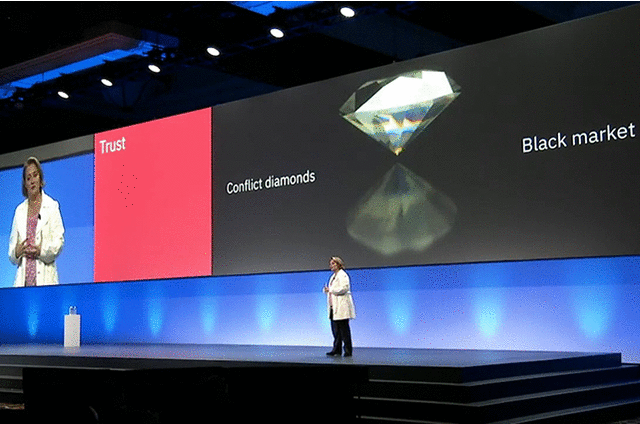
Another vendor, Everledger uses blockchain on LinuxONE to do away with risky paper-based certification systems used in the tracking and authenticating of diamonds. The company now has 1.2 million diamonds secured on the blockchain.
“We built a platform that enables us to be able to bring greater transparency to the open marketplaces and global supply chain by ensuring that the authenticity of the asset is secured and stored amongst all industry participants.” —Leanne Kemp, Everledger
Identity management
IBM and SecureKey Technologies are working together to bring identity management into blockchain. The collaboration aims at developing a new network for digital identity and attribute sharing based on IBM Blockchain.
According to IBM, the network will be designed to make it easier for consumers to verify they are who they say they are, in a privacy-enhanced, security-rich, and efficient way. Consumers can use the network to instantly verify their identity for services, such as new bank accounts, driver’s licenses, or utilities.
Currently still in the testing phase, the network is expected to go live in Canada later in 2017. Canadian consumers will be able to opt-in to the new blockchain-based service using a mobile app.What IBM is building with SecureKey and members of the digital identity ecosystem in Canada, including major banks, telecom companies, and government agencies, will help tackle the toughest challenges surrounding identity.” —Marie Wieck, IBM
Blockchain for energy
IBM and Energy-Blockchain Labs have developed the first blockchain-based green asset management platform based on Hyperledger Fabric v1.0. The platform looks to assist enterprises minimize carbon emissions.
The platform is now being used in China where Energy-Blockchain Labs and IBM look to decrease the country’s whopping 28.21% of the global CO2 emission in 2016.“It is estimated that the platform will significantly shorten the carbon assets development cycle and reduce the cost of it by 20 to 30 percent, enabling cost-effective development of a large number of carbon assets.”
—Cao Yin, Energy-Blockchain Labs
Beijing Energy Chain is also using IBM Blockchain to develop a carbon asset management system.
Blockchain for IoT
According to John Cohn, blockchain is going to completely transform IoT and the world around us—increasing trust, accountability, and transparency.
"In my 35 years as a scientist in IBM, I have never seen a technology ascend to be so instrumental in biz as #blockchain" #ibminterconnect pic.twitter.com/8my9nniAw8
— IBM WatsonIoT (@IBMIoT) March 20, 2017
Using IBM Watson and blockchain, Walmart is building a supply chain to track shipments.
Walmart is building their new transformation strategy with #WatsonIoT and IBM Blockchain. #ibminterconnect pic.twitter.com/hSkfxyO41M
— IBM WatsonIoT (@IBMIoT) March 20, 2017
Boeing follows the same pattern to manufacture and deliver airplanes.
Learning from #Boeing and their #IoT + #Blockchain journey #watson #ibminterconnect pic.twitter.com/T7LoB2leL2
— Alberto Miyazaki (@aamiyazaki) March 20, 2017
Blockchain’s potential in aviation industry is truly impressive, as already recognized by many airlines, such as Airbus, which has joined the Hyperledger project recently.
With IoT, AI, and machine learning being key trends during the conference, it doesn’t come as a surprise that cognitive blockchains are on the IBM drawing boards.
With the combination of IBM Blockchain and Watson, will we see the evolution of smart contracts into cognitive contracts that continually learn and adapt as business data and regulations change? Will we see the use of intelligent agents to perform tasks for business networks to stay ahead of malicious activities? IBM believes so.
Related videos
Further reading
- IBM InterConnect: Bringing in Secure, Hybrid, and Multi-Cloud Infrastructures
- IBM: The Time for IoT, AI, and Machine Learning Is Now
About the speakers