Discussing TensorFlow History, Challenges, and Learning Perspective
![]()
TensorFlow is an open-source machine learning library originally developed by Google. The solution’s flexible architecture allows for deploying computation to one or more CPUs or GPUs in a desktop, server, or mobile device with a single API.
Watch the videos from the TensorFlow Silicon Valley meetup—sponsored and organized by Altoros on January 19, 2016.
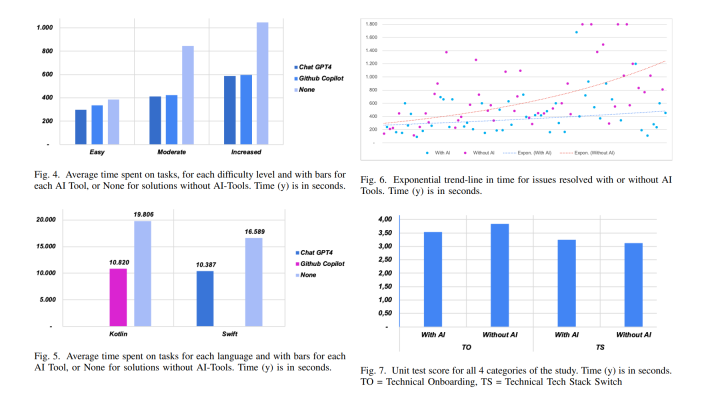
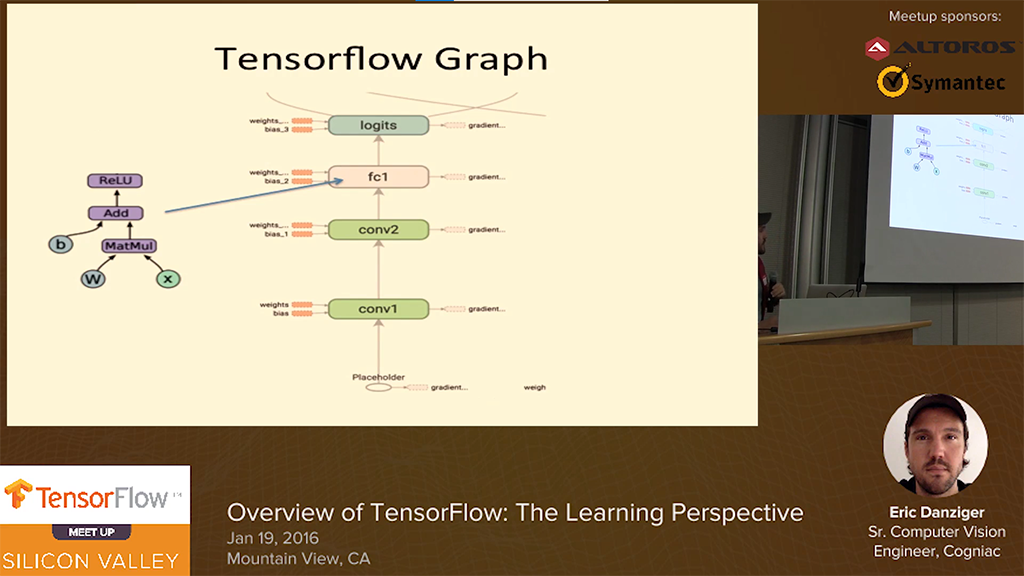
TensorFlow overview: The learning perspective
In this video, Eric Danziger, Senior Engineer at a computer vision startup in San Jose, shared his experience of learning TensorFlow. He started with the MNIST demo and worked up to replicating parts of the “Playing Atari with Deep Reinforcement Learning” paper by Volodymyr Mnih et al.
An end-to-end example of using TensorFlow
In his talk, Delip Rao of Joostware focused on under-the-hood mechanisms of TensorFlow with an actual code example. His goal was to demonstrate various TensorFlow concepts in the context of a working application.
Fireside chat with the Google Brain team
This session with Yaroslav Bulatov and Lukasz Kaiser of the Google Brain team overviews the formation of TensorFlow in brief, provides some examples of the tool applied within Google products, plans for the future, etc. Highlights:
- The history behind the project
- Examples of TensorFlow behind the Google products
- Problems that can be solved with TensorFlow
- The most exciting thing about TensorFlow
- The feedback from the external stakeholders and actions taken
- How TensorFlow becoming open-source changed the roadmap
- The plans for the future in terms of multi-GPU cloud deployments
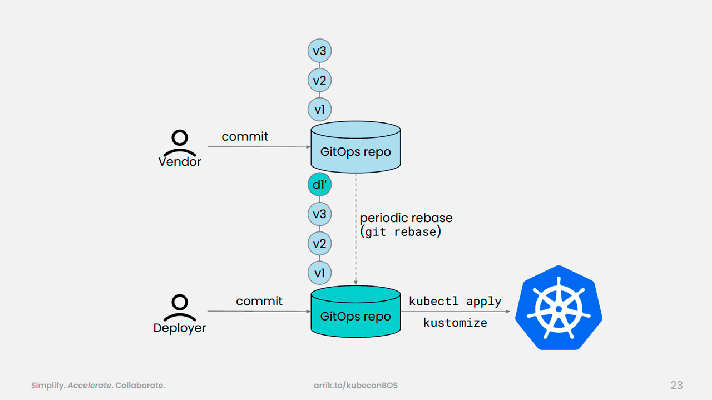
- How the “kubernetization” of TensorFlow happens
- The DevOps aspect of TensorFlow: issues to handle
- The problems TensorFlow is really good at solving or will be able in the future
- The biggest challenges TensorFlow has right now and the resolutions to come in the next 3–6 months
Fireside chat: OpenAI and the future of deep learning
Gregory Renard, Chief Visionary Officer at XBrain—the company designing assistance for automakers, talked about OpenAI and the future of deep learning. (OpenAI is a non-profit artificial intelligence research organization founded by recognized machine learning/AI research engineers and scientists.) He highlighted the following aspects:
- The problems the automotive / insurance industries face and how XBrain helps to solve them.
- How and why such an organization as OpenAI can change the situation, where most of the practitioners in the deep learning are employed by a handful of companies.
- The big trends in deep learning and how they are changing the future.
- The industries that can benefit from the work of such an organization as OpenAI.
See you at the next meetups!
Further reading
- Performance Benchmark: Caffe, Deeplearning4j, TensorFlow, Theano, and Torch
- Mastering Game Development with Deep Reinforcement Learning and GPUs
- How to Set Up a GPU-Enabled TensorFlow Instance on AWS
- TensorFlow in the Cloud: Accelerating Resources with Elastic GPUs
About the experts