Performance Evaluation: MongoDB over NetApp E-Series
NetApp, a provider of high-performing data storage systems, has been working on adjusting its offerings to the requirements of NoSQL databases,such as MongoDB. As a result, the company now offers two MongoDB-certified flash storage solutions. Altoros joined the effort to evaluate these products.
This blog post reveals some of the performance results for the MongoDB integrated architecture deployed to NetApp E-Series.
Overview of the tested scenarios
The examined system design employs a highly effective and scalable MongoDB cluster empowered with the additional storage reliability provided by E-Series. The results shed light on both performance and recovery after a disk failure. A sharded MongoDB cluster over NetApp E-Series E5600 was tested under the following scenarios.
- All-SSD drives (equivalent to an EF560)
- HDD drives employing SSD drives for read acceleration (SSD Read Cache)
- E5600 configured with Dynamic Disk Pools (DDP) for enhanced recovery times when a drive fails (performance on failure)
Testing SSD cache
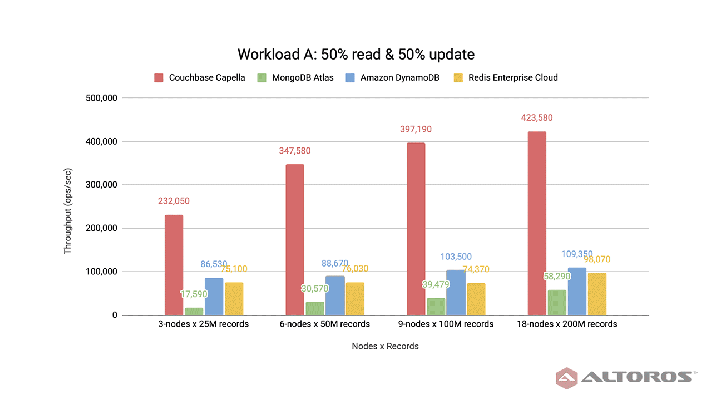
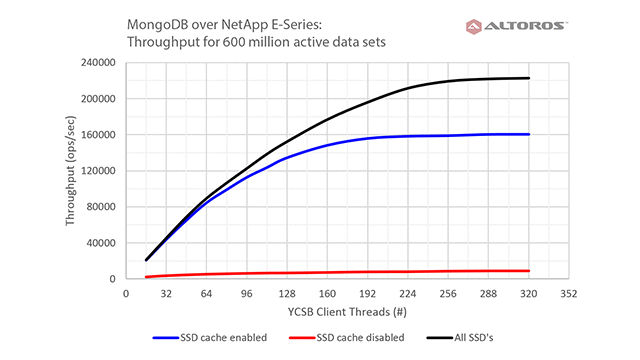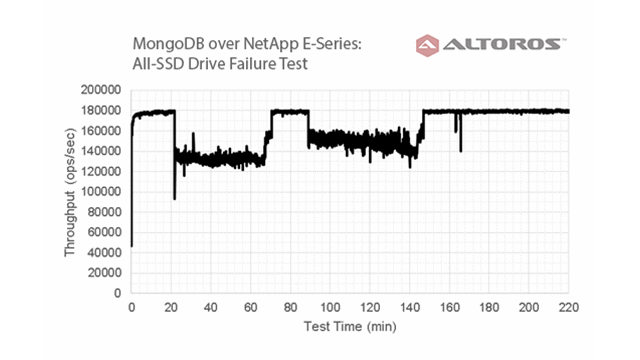
The new SSD Read Cache feature was the most promising to the NoSQL team at Altoros, since it serves as a candidate to improve HDD-backed deployment performance close to the one observed for the all-SSD configuration. The diagram below demonstrates some of the results.
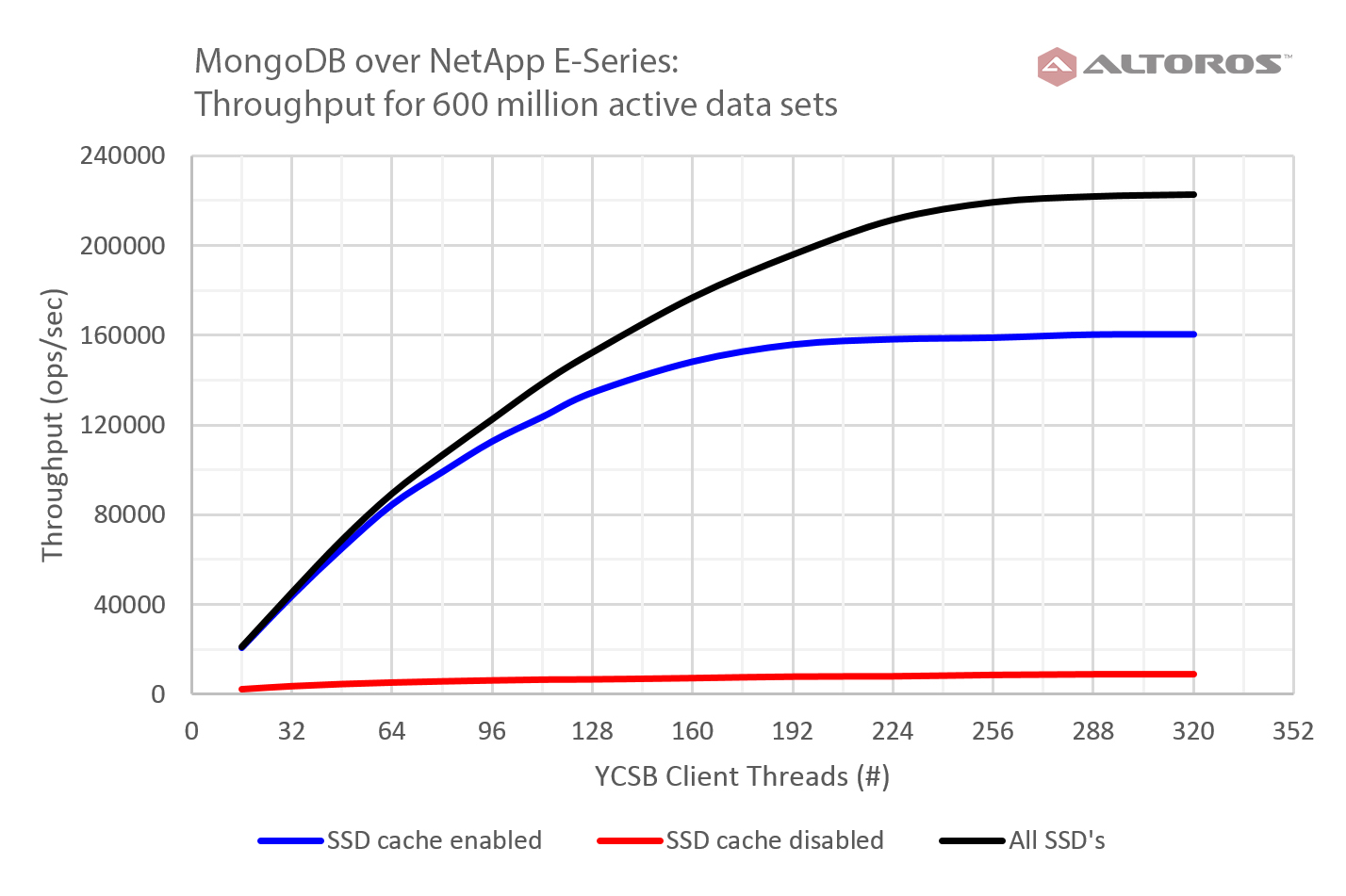 SSD cache test results
SSD cache test results
Disk failure recovery
The following diagram illustrates fast recovery after a disk failure, as well as increased overall storage manageability.
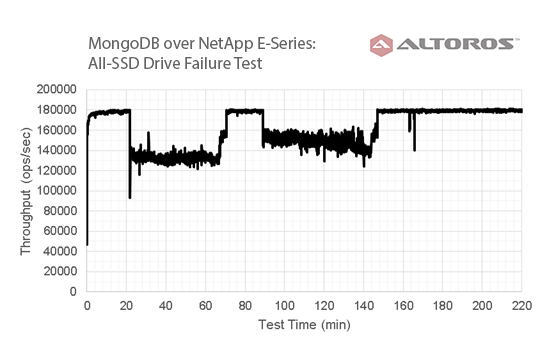 All-SSD drive failure test results
All-SSD drive failure test results
Conclusion
This way, when implemented for high-load MongoDB deployments, NetApp E-Series outranks direct-access storages against a number of criteria. One of the main advantages is the opportunity to use a regular HDD storage armed with an SSD-based cache. In addition to low latencies and high throughput, the NetApp E-Series integrated architecture for MongoDB provides rapid rebuild after disk failures and other operational advantages.
For the result of performance tests, check out this 25-page technical report.